
There are six muscles present in the eye: Medial Rectus, Lateral Rectus, Superior Rectus, Inferior Rectus, Superior Oblique, Inferior Oblique.Some of the most important parts of the eye are: Sclera, Retina, Cornea, Iris, Pupil, Lens etc.It is composed of two segments fused together. The structure of the human eye is roughly spherical.It allows us to see and perceive objects, distinguish color and acts as a biological clock. Human Eye is the vision providing organ of the body.
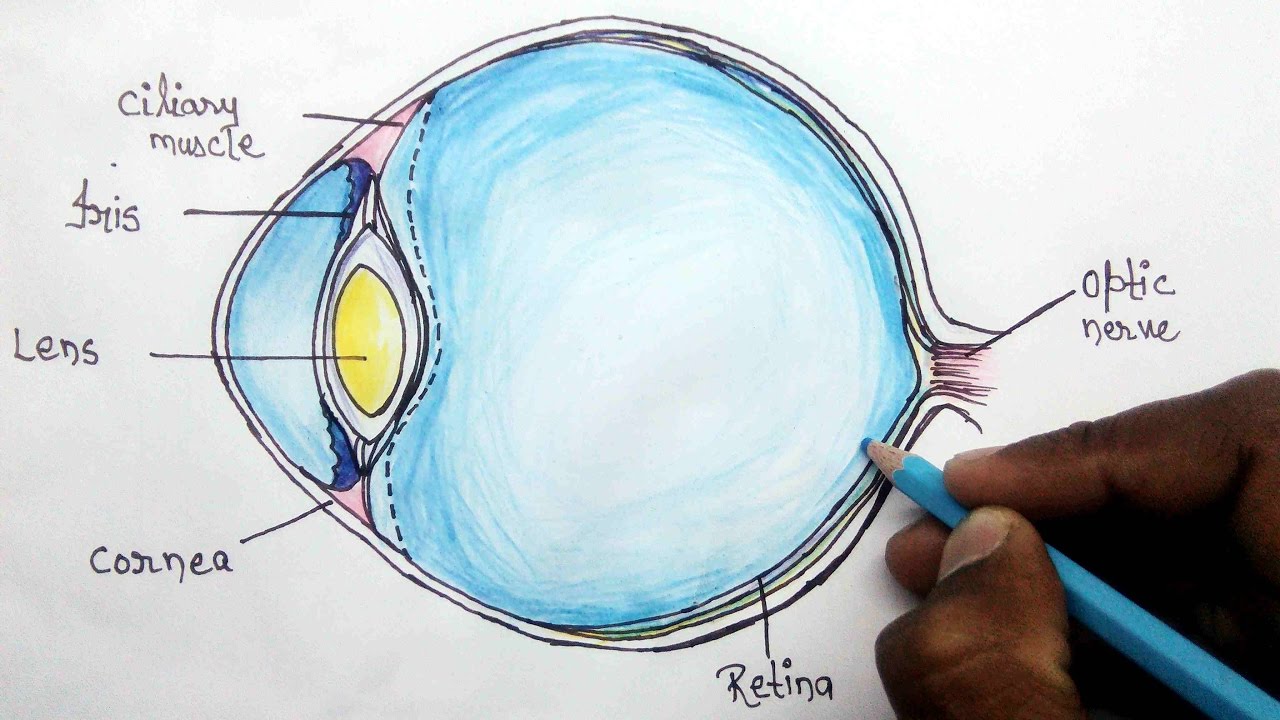
The brain processes the impulses and reacts accordingly. These impulses are transferred to the brain through the optic nerve. The nerve cells convert the light into electrical impulses. The presence of rod and cone cells in the retina help in detecting the intensity and frequency of the light. Due to the difference in refractive index, the light rays bend and fall on the retina. The refractive index of air is 1 and the refractive index of the cornea is 1.376. It becomes thinner and thicker to focus on distant and nearby objects respectively. The ciliary muscles help in changing the shape of the lens to focus the light on the retina. This is achieved with the help of ciliary muscles. It has the ability to change its refractive power. Lens: Lens is a transparent structure that is situated behind the pupil. It determines the exposure of the eye to light. Pupil: The iris has a small opening called the pupil.

It also controls the exposure of the eye to light by adjusting the size of the pupil. Iris: The iris is situated behind the cornea, in its centre. To protect the eye, the cornea has a surrounding of tear fluids that are produced in the tear glands. Due to the curvature of the cornea, it refracts the light up to around 45 dioptres. The Cornea is thinner in the centre and its thickness increases as you move outwards. It is the outermost protective layer of the eye.Ĭornea: The front-facing transparent part of the eye is called Cornea. Sclera: The outer white part of the eye is called Sclera.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
